In a world where connectivity is crucial, understanding how subnetting and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) notation work is fundamental for network engineers and developers. These tools optimize IP address usage, divide networks efficiently, and ensure seamless communication between devices. This article provides an expanded guide with detailed tables and clear explanations of these essential concepts.
CIDR and Subnet Mask Reference Table
The following table provides a quick reference for subnet masks, wildcard masks, and the number of available IP addresses for different CIDR configurations:
| CIDR | Subnet Mask | Wildcard Mask | # of IP Addresses | # of Usable IP Addresses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /32 | 255.255.255.255 | 0.0.0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| /31 | 255.255.255.254 | 0.0.0.1 | 2 | 2* |
| /30 | 255.255.255.252 | 0.0.0.3 | 4 | 2 |
| /29 | 255.255.255.248 | 0.0.0.7 | 8 | 6 |
| /28 | 255.255.255.240 | 0.0.0.15 | 16 | 14 |
| /27 | 255.255.255.224 | 0.0.0.31 | 32 | 30 |
| /26 | 255.255.255.192 | 0.0.0.63 | 64 | 62 |
| /25 | 255.255.255.128 | 0.0.0.127 | 128 | 126 |
| /24 | 255.255.255.0 | 0.0.0.255 | 256 | 254 |
| /23 | 255.255.254.0 | 0.0.1.255 | 512 | 510 |
| /22 | 255.255.252.0 | 0.0.3.255 | 1,024 | 1,022 |
| /21 | 255.255.248.0 | 0.0.7.255 | 2,048 | 2,046 |
| /20 | 255.255.240.0 | 0.0.15.255 | 4,096 | 4,094 |
| /19 | 255.255.224.0 | 0.0.31.255 | 8,192 | 8,190 |
| /18 | 255.255.192.0 | 0.0.63.255 | 16,384 | 16,382 |
| /17 | 255.255.128.0 | 0.0.127.255 | 32,768 | 32,766 |
| /16 | 255.255.0.0 | 0.0.255.255 | 65,536 | 65,534 |
| /15 | 255.254.0.0 | 0.1.255.255 | 131,072 | 131,070 |
| /14 | 255.252.0.0 | 0.3.255.255 | 262,144 | 262,142 |
| /13 | 255.248.0.0 | 0.7.255.255 | 524,288 | 524,286 |
| /12 | 255.240.0.0 | 0.15.255.255 | 1,048,576 | 1,048,574 |
| /11 | 255.224.0.0 | 0.31.255.255 | 2,097,152 | 2,097,150 |
| /10 | 255.192.0.0 | 0.63.255.255 | 4,194,304 | 4,194,302 |
| /9 | 255.128.0.0 | 0.127.255.255 | 8,388,608 | 8,388,606 |
| /8 | 255.0.0.0 | 0.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 | 16,777,214 |
(*Note: /31 is a special case for point-to-point links as detailed in RFC 3021).
Subnet Masks and Wildcards: Decimal to Binary
This table helps illustrate how subnet masks are converted to binary and their corresponding wildcard masks:
| Subnet Mask | Wildcard Mask |
|---|---|
| 255.255.255.255 | 0.0.0.0 |
| 255.255.255.254 | 0.0.0.1 |
| 255.255.255.252 | 0.0.0.3 |
| 255.255.255.248 | 0.0.0.7 |
| 255.255.255.240 | 0.0.0.15 |
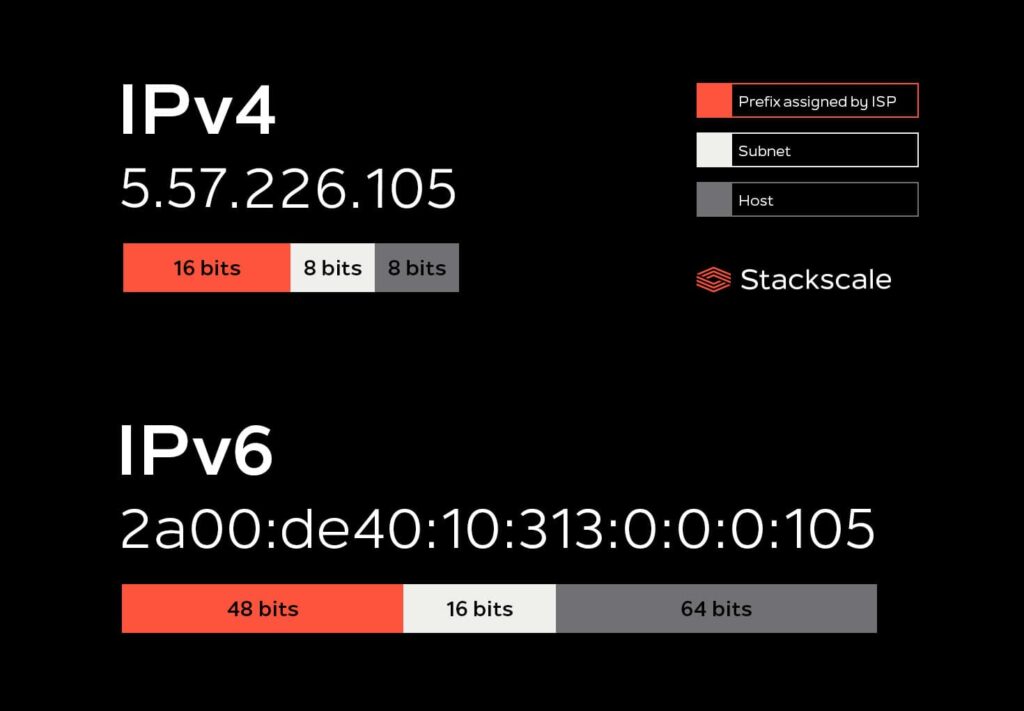
What is Subnetting?
Subnetting is a process that allows a large network to be divided into smaller sub-networks or subnets, optimizing IP address usage. This technique is essential for efficiently managing resources in both enterprise and home networks.
For example, a home network with the IP range 192.168.1.0/24 can be divided into smaller subnets like 192.168.1.0/26 and 192.168.1.64/26, assigning a group of IP addresses to different departments or devices.
Advantages of CIDR
CIDR, introduced in 1993, replaced the rigid class-based IP addressing system. Its benefits include:
- Efficient IP Utilization: Allows for networks of customized sizes, reducing waste.
- Flexibility: Supports subnetting within subnets.
- Scalability: Enables network growth without redesigning the infrastructure.
How to Calculate CIDR Notation
To determine the CIDR notation for a subnet mask, convert the mask into binary and count the number of “1” bits. For instance:
| Type | Decimal | Binary |
|---|---|---|
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.0 | 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 |
Here, there are 24 “on” bits, so the CIDR notation is /24.
Conclusion
Understanding subnetting and CIDR notation is vital in modern network design. These tools maximize IP address usage, improve device communication, and ensure scalability in an increasingly connected environment. The guide and tables provided here serve as an invaluable reference for professionals in telecommunications and IT.

